I’ve written before about how to protect WordPress XML-RPC and why it’s important. In this quick post, I explain three easy ways to to disable WordPress XML-RPC to help improve the security of your WordPress-powered site. Continue reading »
![[ Stormtroopers Keeping Things Secure. ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2019/security-obscurity.jpg)
ob·scure adjective 1. not discovered or known about; uncertain. In the purely literal sense, the concept of obscurity applies to every transaction on the Web. The HTTP request knows not, nor could possibly know, the actual response it will receive from the server. There is only expected response. Online nothing is certain until it is. Continue reading »
![[ Automatic IP Blacklist ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2018/automatic-ip-address-blacklist.jpg)
Recently a reader going by the name of Rock Star sent me a cool little PHP script that automatically updates your site’s .htaccess with a current list of bad IP addresses. This is useful because it gives you better “real time” protection against attacks and malicious requests. This tutorial shares the code and explains how to implement in two easy steps. Continue reading »
![[ Watch Cyber Attacks Online ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2017/cyber-threat-map.jpg)
Taking a quick break to watch cyber attacks happening in real time. Continue reading »
Typically malicious scans use some sort of encoding to obscure their payloads. For example, instead of injecting a literal script, the attacker will run it through a PHP encoding function such as base64_encode(), utf8_encode(), or urlencode(). So if and when you need to decode some discovered payload, you can use whichever decoding function will do the job. For example, base64_decode(), utf8_decode(), or urldecode(). Sounds straightforward, but let’s dig a little deeper.. Continue reading »
It was recently reported about a WordPress Pingback Vulnerability, whereby an attacker has four potential ways to cause harm via xmlrpc.php, which is the file included in WordPress for XML-RPC Support (e.g., “pingbacks”). In this post, I offer a simple .htaccess technique to lock things down and protect against any meddling via the xmlrpc.php file. Continue reading »
![[ Prise de la Bastille, by Jean-Pierre-Louis-Laurent Houel (Detail) ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2012/tale-hacked-website.jpg)
I love a good story. Almost as much as I enjoy securing websites. Put them together and you’ve got suspense, intrigue, and plenty of encoded gibberish. But no happy ending this time, in this case the smartest decision was to “pull it” and rebuild. The site was just wasted — completely riddled with malicious code. Without current backup data, it would’ve been “game over” for the site, and possibly the business. Continue reading »
![[ Decoding PHP ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2012/decoding-php-code.jpg)
There are many ways to encode and decode PHP code. From the perspective of site security, there are three PHP functions — str_rot13(), base64_encode(), and gzinflate — that are frequently used to obfuscate malicious strings of PHP code. For those involved in the securing of websites, understanding how these functions are used to encode and decode encrypted chunks of PHP data is critical to accurate monitoring and expedient attack recovery. Continue reading »
![[ Screenshot: malicious iframe injected into web page ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2012/video-player-swfobject.gif)
During the recent redesign, I discovered that my newer WP installation (v3.3.1) had been hacked. I get this email first thing in the morning: Continue reading »
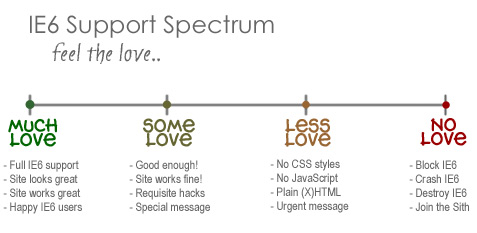
I know, I know, not another post about IE6! I actually typed this up a couple of weeks ago while immersed in my site redesign project. I had recently decided that I would no longer support that terrible browser, and this tangential post just kind of “fell out.” I wasn’t sure whether or not to post it, but I recently decided to purge my draft stash by posting everything for your reading pleasure. Thus, you may see a few turds […] Continue reading »
In my previous article on redirecting 404 requests for favicon files, I presented an HTAccess technique for redirecting all requests for nonexistent favicon.ico files to the actual file located in the site’s web-accessible root directory: # REDIRECT FAVICONZ <ifmodule mod_rewrite.c> RewriteCond %{THE_REQUEST} favicon.ico [NC] RewriteRule (.*) http://domain.tld/favicon.ico [R=301,L] </ifmodule> As discussed in the article, this code is already in effect here at Perishable Press, as may be seen by clicking on any of the following links: Update: I’ve removed the […] Continue reading »
For the last several months, I have been seeing an increasing number of 404 errors requesting “favicon.ico” appended onto various URLs: http://example.com/favicon.ico http://example.com/2007/06/12/favicon.ico http://example.com/2007/09/25/absolute-horizontal-and-vertical-centering-via-css/favicon.ico http://example.com/2007/08/01/temporary-site-redirect-for-visitors-during-site-updates/favicon.ico http://example.com/2007/01/16/maximum-and-minimum-height-and-width-in-internet-explorer/favicon.ico When these errors first began appearing in the logs several months ago, I didn’t think too much of it — “just another idiot who can’t find my site’s favicon..” As time went on, however, the frequency and variety of these misdirected requests continued to increase. A bit frustrating perhaps, but not serious enough to […] Continue reading »
Just a quick WordPress snippet for future reference. I recently explained how to disable comments, pingbacks, and trackbacks via SQL. Here’s a good way to do it via PHP: <?php function close_comments( $posts ) { if ( !is_single() ) { return $posts; } if ( time() – strtotime( $posts[0]->post_date_gmt ) > ( 30 * 24 * 60 * 60 ) ) { $posts[0]->comment_status = 'closed'; $posts[0]->ping_status = 'closed'; } return $posts; } add_filter( 'the_posts', 'close_comments' ); ?> You can run […] Continue reading »
![[ Exclude Feed Content ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2008/misc-chunks/exclude-feed-content.png)
This may surprise you, but I post quite a bit of content that never appears in the site’s main feed. It is my impression that a vast majority of subscribers are interested in web/graphic-design and development-related topics, and are really much less interested (if at all) in the miscellaneous odds and ends that wind up in the ever-expanding Perishable Press database. In the past, the process of excluding content from the main feed typically involved changing the post-date to something […] Continue reading »
Continuing my quest to stop comment spam without using plugins, I have decided to disable comments on “old” posts. In my experience, over 90% of comment, trackback and pingback spam occurs on posts that have been online for over a month or so, just long enough to be indexed by the search engines and picked up by spammers. Especially for older posts that have managed to acquire a little page rank, the frequency of spam attempts is far greater than […] Continue reading »
![[ WordPress Core Hacks ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2007/misc-chunks/wp-core-hacks.jpg)
One of the necessary evils associated with creating a highly customized WordPress-powered site involves the inevitable necessity to hack the WordPress core. WordPress is built for mass-consumption and tends to cater to the largest audience possible, making it necessary to bend and poke around the corners to get WordPress to function in a more specific or specialized capacity. Continue reading »

![[ Stormtroopers Keeping Things Secure. ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2019/security-obscurity.jpg)
![[ Automatic IP Blacklist ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2018/automatic-ip-address-blacklist.jpg)
![[ Watch Cyber Attacks Online ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2017/cyber-threat-map.jpg)
![[ Prise de la Bastille, by Jean-Pierre-Louis-Laurent Houel (Detail) ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2012/tale-hacked-website.jpg)
![[ Decoding PHP ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2012/decoding-php-code.jpg)
![[ Screenshot: malicious iframe injected into web page ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2012/video-player-swfobject.gif)

![[ Exclude Feed Content ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2008/misc-chunks/exclude-feed-content.png)
![[ WordPress Core Hacks ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2007/misc-chunks/wp-core-hacks.jpg)
