
Book Launch! My fourth book, WordPress Themes In Depth, focuses entirely on WordPress theme development. It goes in-depth on how to build, customize, and distribute your own WordPress themes. It’s 10+ years of experience with WordPress jam-packed into 450 pages of non-stop theme-building action. Continue reading »
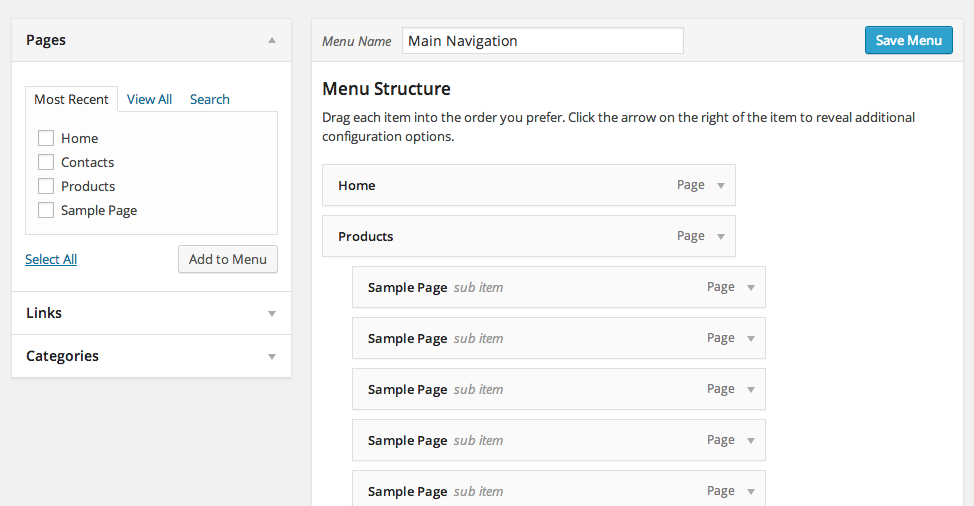
In this tutorial I am going to show you how to build a pure CSS drop down menu in WordPress. I will walk you through the steps of creating a menu in WordPress, customizing it with CSS, and then printing the menu in your theme file. This tutorial requires that you have access to edit your WordPress theme files and also a basic understanding of HTML and CSS. I will walk through the process step-by-step so don’t worry if you […] Continue reading »
![[ Protect yourself ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2014/gas-mask-dog.jpg)
Whether you like it or not, there are scripts and bots out there hammering away at your sites with endless HTTP “POST” requests. POST requests are sort of the opposite of GET requests. Instead of getting some resource or file from the server, data is being posted or sent to it. To illustrate, normal surfing around the Web involves your browser making series of GET requests for all the resources required for each web page. HTML, JavaScript, CSS, images, et […] Continue reading »
I woke up this morning to the sound of thousands of 404 requests hitting the server. It’s sad that there are kiddies out there who have nothing better to do than buy some pathetic $50 script and then sit there like an imbecile harassing people for hours on end. But alas, that is the world we live in — fortunately it’s less than trivial to block the entire scan with just a few lines of good old .htaccess. Continue reading »
![[ WP Plugin: Core Control ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2014/core-control.gif)
Just a quick post with some tips for troubleshooting and testing HTTP requests. For example, if you have a plugin that sends requests behind the scenes via Ajax or cURL or whatever, it’s nice to have a way to view request details such as headers, the response, and everything in between. This article is aimed primarily at WordPress users, but contains more general tips and tricks as well. Continue reading »
![[ 2014 Micro Blacklist ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2014/micro-blacklist.jpg)
Over the past several months, I’ve assembled a “micro” blacklist to keep some recent threats at bay. Eventually, this will be integrated into the next nG Blacklist, but for now I just wanted to post and share with anyone else who is actively monitoring their server logs and aware of the recent spike in malicious activity. Continue reading »
Another update! This time to the vanilla/PHP version of my Ajax Error Log. As with the new WordPress version, this update improves the script’s design, performance, and security. Continue reading »
New version of Ajax-Powered Error Logs for WordPress now available for download. The functionality is the same, but the script is rewritten for better design, performance, and security. Continue reading »
![[ 2013 User Agent Blacklist ]](/wp/wp-content/images/2013/user-agent-blacklist.png)
The 2013 User Agent Blacklist blocks hundreds of the worst bots while ensuring open-access for normal traffic, major search engines (Google, Bing, et al), good browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Opera, et al), and everyone else. Compared to blocking threats by IP, blocking by user-agent is more effective as a general security strategy. Although it’s trivial to spoof any user agent, many bad requests continue to report user-agent strings that are known to be associated with malicious activity. For example, the notorious […] Continue reading »
When time allows, I like to post my collections of the worst IP addresses for the current year. Certainly, there are pros and cons to using an IP blacklist. In general, IPs are easily spoofed, change frequently, and are therefore unreliable as a general security strategy. But as a short-term solution, IP blacklists serve as an excellent method for dealing with specific and/or ongoing threats and attacks. Continue reading »
![[ The Tao of WordPress ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2013/tao-of-wordpress.jpg)
It’s been quiet around here, but I have a good excuse. I spent the last six months writing, designing, and publishing my third book, The Tao of WordPress. This is an excellent book for beginners, students, designers, and basically anyone who wants to learn how to get the most from WordPress. The book “soft-launched” last week, and now I want to share the news with readers here at Perishable Press. Continue reading »

In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to install and run WordPress MultiSite on a MAMP webserver. Running multiple sites from a single installation simplifies and streamlines administration, and serving it all from a locally installed version of MAMP gives you everything you need to develop your network of sites for the Web. Continue reading »
![[ 5G (2013) ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2013/5G-Blacklist.png)
Following up on much feedback (and this post), here is an update for the 5G Blacklist for 2013. As explained in the 2012 article (and elsewhere), the 5G Blacklist helps reduce the number of malicious URL requests that hit your website. It’s one of many ways to improve the security of your site and protect against evil exploits, bad requests, and other nefarious garbage. If your site runs on Apache and you’re familiar with .htaccess, the 5G is an effective […] Continue reading »
Just as there are specifications for designing with CSS, HTML, and JavaScript, there are specifications for working with URIs/URLs. The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) clearly defines these specifications in RFC 3986: Uniform Resource Identifier (URI): Generic Syntax. Within that document, there are guidelines regarding which characters may be used safely within URIs. This post summarizes the information, and encourages developers to understand and implement accordingly. Continue reading »
![[ Blacklist Candidate Props ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2012/bob-barker.jpg)
It’s been awhile since I’ve posted one of my Blacklist Candidate series articles. It’s always fun for me to talk (or write) about security related issues, especially when a quick slab of .htaccess can be used to take care of business. And that’s exactly what we have in this edition of the series, where I’m pleased to bring you Blacklist Candidate Number 2012-11-13: the “evil” scanner. Instead of scanning your site, collecting data, and moving on, Mr. 2012-11-13 continues to […] Continue reading »

BBQ Firewall is a lightweight, super-fast plugin that protects your site against a wide range of threats. BBQ checks all incoming traffic and quietly blocks bad requests containing nasty stuff like eval(, base64_, and excessively long request-strings. This is a simple yet solid solution for sites that are unable to use a strong Apache/.htaccess firewall. Continue reading »



![[ Protect yourself ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2014/gas-mask-dog.jpg)
![[ WP Plugin: Core Control ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2014/core-control.gif)
![[ 2014 Micro Blacklist ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2014/micro-blacklist.jpg)
![[ 2013 User Agent Blacklist ]](/wp/wp-content/images/2013/user-agent-blacklist.png)
![[ The Tao of WordPress ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2013/tao-of-wordpress.jpg)

![[ 5G (2013) ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2013/5G-Blacklist.png)
![[ Blacklist Candidate Props ]](https://perishablepress.com/wp/wp-content/images/2012/bob-barker.jpg)

